
Building Management SystSystem Controls, also known as a building management system (BMS) is a software application that automates the operations and management of a complex structure or facility. It coordinates and manages all aspects of the building, from energy use to maintenance schedules, ensuring that it operates safely and efficiently. A BMS can integrate with existing systems to automate more tasks, creating a truly integrated approach to building management.
A BMS typically comprises several modules:
An overview of each module is provided below.
1) Operations – This module includes features such as scheduling, tracking, and reporting related to building operations.
2) Maintenance – This module allows for the automation of repairs, inspections, and updates to the building’s systems and components.
3) Security – This module provides features such as security patrols and reports on secure areas within the facility.
4) Energy – This module manages energy usage in the building, including features such as energy audits and rebates.
5) Analytics – This module allows for analysis of data collected by other modules in order to improve efficiency and performance.
A building management system (BMS) provides a comprehensive system for managing all aspects of the operation and maintenance of buildings. A BMS can provide information on energy usage, occupancy, equipment status, and more. The goal of a BMS is to improve efficiency and safety in buildings.
A BMS should include controls to ensure that the data collected is accurate and timely. Controls may include user authorization requirements, data quality checks, and security measures. A BMS can also help to optimize energy use by providing real-time information on energy consumption in individual rooms or areas.
A BMS is a sophisticated and important piece of software that helps to ensure reliable operations by managing vital processes and systems. Some of the functions of a BMS include:
1. Process control – A BMS can track and manage critical processes throughout an organization, ensuring that they are carried out in a consistent and controlled manner. This ensures that all aspects of the organization’s operation are managed in an effective and efficient manner.
2. Data management – A BMS can organize and store data in a secure fashion, allowing managers to access it quickly and easily. This allows them to monitor trends and make informed decisions regarding business operations.
3. Security monitoring – A BMS can help protect against unauthorized access to data and systems, ensuring that information remains confidential. This helps to safeguard company assets and keep customers safe.
4. Operational planning – A BMS can help managers plan future operations, ensuring that developments are accurately reflected in the system. This allows for smooth running of the business overall
Building automation and control systems (BACS) are becoming more popular as builders and property managers seek to improve the efficiency, safety and comfort of buildings. Automated systems can improve building management by providing controls for heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, security and communications.
There are a variety of types of BACS available, including standalone systems, hybrid systems and integrated systems. Some common features of BACS include:
– Automation of building operations
– Control over HVAC & lighting systems
– Monitoring & reporting capabilities
– Integration with other building systems
A building management system (BMS) is a collection of computer applications that manage the operational aspects of buildings. BMSs are typically used to control energy usage, maintain temperature and humidity levels, track occupancy, dispense materials, and monitor security. A building automation system (BAS) is a subset of a BMS that mainly controls building operations through automated systems and devices.
The two systems have different purposes and should be used in conjunction with each other. A BAS should be used to automate tasks that do not require human interaction such as lights turning on or off, heating or cooling schedules, or door openings/closings. A BMS should be used to manage all other functions such as scheduling maintenance tasks or detecting security breaches.
A Smart Building is a building that has been designed to optimize energy use and performance, create a comfortable environment, and make occupant mobility easier. It uses intelligent controls and automation so that it can operate more efficiently and reduce costs. There are many benefits to having a Smart Building, including:
– Reduced Energy Costs: Buildings use a lot of energy, and a Smart Building can cut down on this by using smart controls that can manage things like ventilation and lighting.
– Increased Comfort: A Smart Building will be able to control temperature and humidity levels, providing a more comfortable environment for occupants.
– Enhanced Mobility: A Smart Building will have features like elevators that allow people with disabilities access easily.
Building management systems (BMS) are a growing trend in the building industry. They provide organizations with an efficient and comprehensive system to track, monitor and manage their buildings.
What is a BMS? A BMS is a computerized system that collects data from various building elements and then processes it to generate reports or alerts. This data can include things like temperature, humidity, energy use, occupancy levels and more. BMSs typically come with several built-in controls to help keep your buildings running smoothly.
How do BMS Systems Work? In short, a BMS uses sensors to collect data from various aspects of a building and then stores it in a database. This information can then be used to generate reports or alerts that are sent to users via email, text message or even social media channels. Controls included with most BMSs can help you keep your buildings operating at peak performance by monitoring things like temperature, humidity and energy use.
A building management system (BMS) is a system that manages the operational aspects of a building. This could include things like monitoring equipment, controlling ventilation and heating, and managing building resources. BMS systems can be used in a variety of settings, such as commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and energy facilities.
A BMS can be broken down into three main components: the data acquisition module (DAM), the controls module, and the communication module. The DAM collects data from various sources within the building and stores it in a centralized location. The controls module allows administrators to manage these data inputs and outputs. The communication module allows administrators to manage communications between the DAM and other elements of the BMS system.
There are several different types of BMS systems available on the market today. Some common types of systems include automated management systems (AMS), digital building automation systems (DBAS), network-enabled building automation systems (NEBAS), software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms, and hybrid architectures. Each type of BMS has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the right one for your specific needs.
One important factor to consider when choosing a BMS is how easy it is to customize or upgrade. Many BMS platforms are cloud-based, which makes them easy to update via software updates or by connecting to an external server. However, some older systems may
Building management systems (BMSs) are used in a variety of buildings, including hospitals, schools, factories, offices, and retail stores. They control the operation and maintenance of a building by managing energy consumption, temperatures, humidity levels, and security.
There are two main types of BMSs: Building automation systems (BAS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. BASs automate tasks such as lighting and air conditioning while ERP systems manage entire fleets of buildings.
Some benefits of using a BMS include reduced energy consumption, improved safety and security, increased efficiency, and reduced costs. However, there are also some potential drawbacks to using a BMS. For example, it can be difficult to integrate an existing system into a new building or to troubleshoot malfunctions. Furthermore, if the BMS is not properly implemented or designed, it can create data silos that make it difficult to share information across departments or between different businesses.
Building Energy Management (BEM)is a process and methodology that helps to optimize energy use in buildings. It recognizes the fact that different parts of the building require different levels of energy, and uses this information to make decisions about which technologies to use, how much energy to use, and when to replace or upgrade equipment.
There are several different types of BEM, but all share some common goals:
To improve overall building efficiency by identifying opportunities for improvement in areas such as lighting, heating/cooling, appliances, and materials selection.
To reduce costs associated with energy use by making informed decisions about which technologies to use, when they should be used, and how much energy they require.
To ensure that the environment in which people work and live is healthy and sustainable.
A building energy management system (BEMS) is a comprehensive system used to optimize the energy use in your facility. A BEMS can help you save money on your energy bills, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and improve indoor air quality.
A BEMS consists of several components, including an energy management system controller, sensors, and meters. The controller is responsible for scheduling and controlling the use of energy in your facility. Sensors monitor various aspects of the environment, such as temperature, humidity, and light levels. Meters track the amount of energy used in your facility.
A BEMS can help you save money on your energy bills by reducing the amount of electricity and gas used in your facility. It can also improve indoor air quality by reducing the amount of pollutants released into the air.
A typical energy management system (EMS) is used to optimize the performance of a building by managing the use of energy. The system can be used to detect and diagnose faults, control loads, and monitor energy usage. An EMS can also help owners & operators reduce their carbon footprints.
There are many different types of EMSs available, but they all have one common goal – to improve the efficiency of a building’s operations. Some of the most common features found in EMSs include:
– Energy monitoring: This allows the system to track energy usage in real time, allowing for immediate detection and correction of any problems.
– Fault detection & diagnosis: If something goes wrong with the energy supply or equipment within a building, an EMS can help identify and correct the issue quickly. This helps prevent costly repairs down the road and saves on energy costs.
– Load management: Using data collected from energy monitoring and fault detection, an EMS can determine when various loads are being put on the grid too often or in excess of what is required. This allows for proactive measures (such as reducing or suspending power usage) to be taken before problems arise.
– Power management: By understanding how much power each load is using and when it is being used, an EMS can automatically adjust power supplies according to prevailing conditions so that all loads are properly served.
A building management system (BMS) is a hardware and software system that manages the operational functions of buildings, including lighting, heating and cooling, security, fire protection and energy management. The BMS coordinates its activities with other systems in the building, such as the Building Automation System (BAS), to achieve desired outcomes.
An energy management control systems (EMCS) is a subset of the BMS that focuses on managing energy use in buildings. An EMCS can include features to optimize energy usage by controlling or monitoring equipment and devices in a building, such as centralized lighting controls or thermal imaging cameras. By understanding how users are using energy, an EMCS can make recommendations for improving efficiency.
Energy management systems (EMS) are a type of control system which helps to optimize the use of energy in an organization. They can help to identify and reduce energy costs, improve efficiency, and protect equipment from damage.
An EMS can provide real-time information about energy usage and performance in an organization, allowing managers to make informed decisions about how to spend their resources. It can also help to predict future needs and manage expectations for energy usage.
There are several different types of EMSs, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Some examples include demand-side management (DSM), load-shedding algorithms, thermal mapping, and smart metering. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to choose the right one for your needs.
If you’re considering installing an EMS in your organization, be sure to speak with a qualified professional. They can help you decide which type of EMS is best suited for your needs and walk you through the installation process.
A building automation system (BAS) is a computerized system that controls various aspects of an office or commercial building. BAS systems can include things like lighting, temperature, security, and ventilation. BAS systems are often connected to other systems in the building, such as the HVAC system, so that they can work together to provide a seamless user experience.
Building automation systems are becoming increasingly popular in commercial and industrial settings. This is due to their many benefits, such as increased safety and efficiency. However, like any other technology, building automation systems can also be exploited for unauthorized access or operations.
One of the most important aspects of securing a building automation system (BAS) is properly configuring the controls. These controls ensure that only authorized users are able to access and operate the system. Additionally, it is important to monitor and maintain the security of the controls themselves. If a hacker gains access to the controls, they can use them to perform unauthorized actions or even undermine the entire BAS system.
To protect your BAS against these types of threats, you need to implement various security measures. Some basic steps include:
– Implementing strong passwords and user accounts: Passwords should be unique and difficult to guess, and users should be required to create new accounts whenever they join a new facility or office.
– Restricting user privileges: Certain BAS functions should only be accessible by designated users with appropriate permissions.
– Installing anti-virus software: Infected files or modules can spread malware within a BAS system, posing a threat to both users and servers.
– Updating virus definitions: As vulnerabilities are discovered and patched, it’s important that you update your virus definitions accordingly.
An industrial control system (ICS) is a comprehensive set of systems and processes used to manage an industrial facility. ICSs are divided into three main categories: plant, process, and platform. Plant ICSs manage the overall operations of plants from initial startup to shutdown. Process ICSs are used to control specific tasks or processes in plants. Platform ICSs allow for the integration of different systems and technologies into a single platform for streamlined management.
The following are seven key principles of operation for an industrial control system:
1. Coordination – All components in an ICS must work together as a coordinated system to achieve desired goals. This includes ensuring that all inputs are properly processed and that outputs are consistent with the desired end state.
2. Communication – All components in an ICS must be able to communicate with each other to share information and resolve conflicts. This communication can take place through built-in mechanisms or through external devices connected to the system via bus, network, or interface cards.
3. Data Management – The data collected by various sensors must be managed and processed in a timely manner so that appropriate decisions can be made based on the current conditions. This includes both collecting data in real time and storing data for future analysis or retrieval.
4. Control Architecture – The control architecture of an ICS must be designed based on the specific needs of the plant being controlled. This includes identifying the types of controls needed,
A building management system (BMS) is a computer-based system that manages the operational aspects of buildings. It includes systems for energy, water, and waste management as well as security and occupancy monitoring.
A BMS integrates with many different systems to provide complete information about the building. These systems include:
Building automation systems (BAS) are often used to control lights, air conditioning, and other building functions. BAS can communicate with a BMS to control these functions automatically.
HVAC controls may be controlled by a BAS or a BMS using remote programming or manual input from users. Temperature settings, fan speeds, and other HVAC parameters can be adjusted from anywhere in the building using this method.
Security systems may use video surveillance footage or sensors to detect intruders or unauthorized activity. The BMS can then send alerts to occupants and security personnel.
The elevator controls may be integrated into the BAS or controlled by the BMS using elevator status data obtained from sensors inside the elevator car. This information can include current elevators in use, number of passengers in each car, and whether the car is in motion or stopped at a floor level.
There are many different suppliers of building management systems (BMS) and controls. This can be confusing, so it is important to choose a supplier that has the knowledge and experience to provide you with the best system.
Some of the main BMS suppliers are:
– Tridium
– Cylon
– Ambiflex
– PRIVA
A Building Performance Report (BPR) is a formal document that summarizes the state of an organization’s indoor environment. The report typically includes data on energy consumption, emissions, and HVAC loads. It can also include information on building materials and construction methods.
The purpose of a BPR is to improve the efficiency and overall health of an indoor environment by identifying problems and making necessary changes. By knowing how your building is performing, you can make informed decisions about how to best maintain it.
There are a few things that you need in order to produce a valid BPR: accurate data, proper instrumentation, and appropriate software. You will also need to have a system in place for collecting and analyzing the data.
Data collection can be done manually or through automated systems. Manual collection involves taking readings from sensors throughout the building and organizing them into reports. Automated systems collect data from sensors using pre-programmed instructions, so there is no human interaction required. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages; manual collection is more labor-intensive but can be more reliable, while automated collection is faster but may not be as accurate.
After reading this guide, you will have a deep understanding of the basics of building management system (BMS) and controls. In this article, you will learn what are BMS and controls, their importance in business, how to develop an effective BMS and controls for your business, and how to deploy them. By the end of this guide, you will be able to create a foundation for designing an effective BMS and controls for your company.
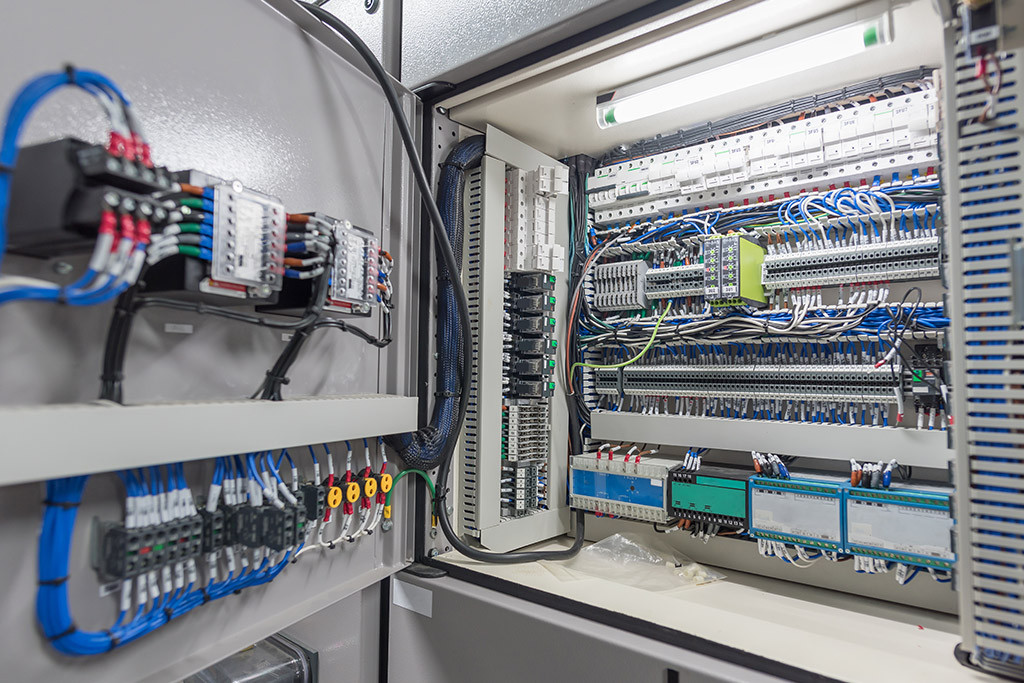
Support and maintenance services are available through us. We can provide ad-hoc support or tailored ongoing support tailored to your needs. In addition, we provide integrated remote support and BMS system monitoring, allowing us to detect issues as soon as they occur. Through thorough analysis of your building’s system, we can recommend optimal actions tailored to your building’s specific environmental conditions.
Copyright © by BMS Control Systems Limited 2023. All right reserved. Company No. 05899420
